Hall Effect Sensor - Measuring strength of magnetic field with Qwiic analog
This page contains a simple example with function documentation on how to take measurements using the SI7211-B-00-IV Hall effect sensor and the Qwiic connection.
Qwiic Analog output example
#include "Hall-Effect-SOLDERED.h"
// To change the reading, place a magnet in front of the sensor
// Declare sensor object on default address
HallEffect_Analog_EasyC hall;
void setup()
{
// Initialize serial communication
Serial.begin(115200);
// Initialize sensor via EasyC (required!)
hall.begin();
// If you wish to use a custom address (e.g. 0x33), use
// hall.begin(0x33);
}
void loop()
{
// Read raw measurement
uint16_t hallRawReading = hall.getRawReading();
// Read milli Teslas
float hallMilliTeslas = hall.getMilliTeslas();
// Print sensor values to serial
Serial.print("Analog Hall Effect raw sensor reading: ");
Serial.println(hallRawReading);
Serial.print("Which is: ");
Serial.print(hallMilliTeslas);
Serial.println(" mT\n");
// Wait a bit until next measurement
delay(1000);
}
HallEffect_Analog_EasyC hall()
Creates analog sensor object
Returns value: none
hall.begin()
Initializes analog sensor object
Returns value: Returns true if initialization is successful, false otherwise.
Function parameters:
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
uint16_t | address | Optional, used for changing breakout address, default is 0x30 |
hall.getRawReading()
Requests a new reading from the SI7211-B-00-IV sensor.
Returns value: Returns int value from output pin
hall.getMilliTeslas()
Calculates the value of magnetic induction from current reading
Returns value: Returns float value that represents magnetic induction in milli Teslas
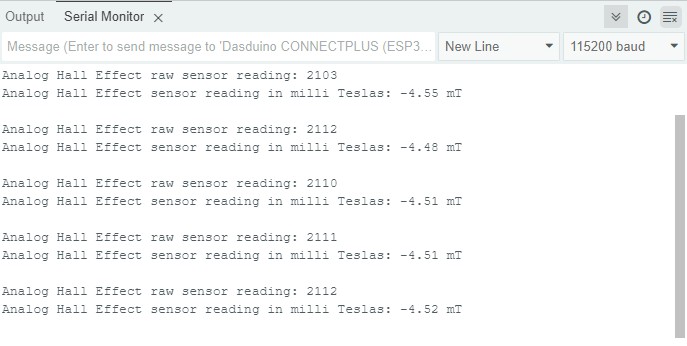
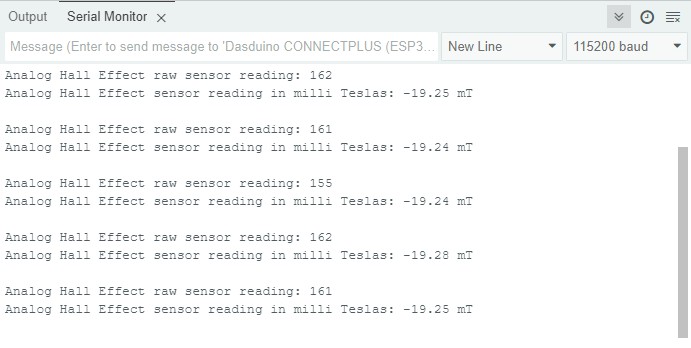
Full example
Try all of the above mentioned functions in this full example which measures the strenght of magnetic field.
analogReadEasyC.ino
Example file for using analog Hall effect sensor with easyC/Qwiic/I2C